Chiba, JAPAN - The National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST), along with Tohoku University and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), succeeded in visualizing of the dynamics of cesium in a living animal using a newly developed positron‑emitting 127Cs tracer for the first time in the world. This research result was published online in SCIENTIFIC REPORTS today.
Highlights
- Production of the positron-emitting nuclide 127Cs by irradiating sodium iodide with a 4He2+ beam.
- Purification of 127Cs tracer using the Cs adsorbent column that excludes sodium ions.
- Successful visualization of the dynamics of cesium (Cs) in a living animal by positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with 127Cs tracer.
After the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company’s Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in March 2011, there has been a growing concern about radiocesium such as 134Cs and 137Cs released into the environment.
Visualizing the dynamics of cesium (Cs) is desirable to understand the impact of radiocesium when accidentally ingested or inhaled by humans. However, visualization of radiocesium in vivo is currently limited to plants. Herein, we describe a method for the production and purification of 127Cs and its use in visualizing Cs dynamics in a living animal.
The positron-emitting nuclide 127Cs was produced using the 127I (α, 4n) 127Cs reaction, which was induced by irradiation of sodium iodide with a 4He2+ beam from a cyclotron. We excluded sodium ions by using a material that specifically adsorbs Cs as a purification column and successfully eluted 127Cs by flowing a solution of ammonium sulfate into the column.
We injected the purified 127Cs tracer solution into living rats and the dynamics of Cs were visualized using positron emission tomography; the distributional images showed the same tendency as the results of previous studies using disruptive methods. Thus, this method is useful for the non-invasive investigation of radiocesium in a living animal.
127Cs tracer will be useful in studies to evaluate internal doses due to radiocesium released into the environment. 127Cs tracer can also be used in plant research to elucidate the mechanism of Cs transport in crops.
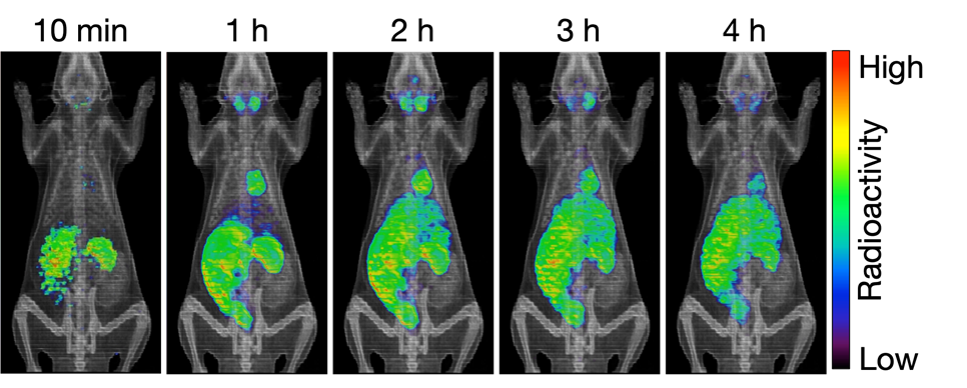
The distribution of Cs in a living animal visualized by PET imaging
This research was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant numbers 16K06962 and 19H04296).
Paper
"Non‑invasive imaging of radiocesium dynamics in a living animal using a positron‑emitting 127Cs tracer”
“SCIENTIFIC REPORTS”: October 15, 2020, doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73351-2
Link (Publication)
Nobuo Suzui1, Takuya Shibata2, Yong‑Gen Yin1, Yoshihito Funaki3, Keisuke Kurita1, Hiroyuki Hoshina1, Mitsutaka Yamaguchi1, Shu Fujimaki1, Noriaki Seko1, Hiroshi Watabe1,3 & Naoki Kawachi1
1 QST, 2 JAEA, 3 Tohoku University
About QST
The National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST) was established in April 2016 to promote quantum science and technology in a comprehensive and integrated manner. The new organization was formed from the merger of the National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS) with certain operations that were previously undertaken by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA).
QST’s mission is to raise the level of quantum and radiological sciences and technologies through its commitment to research and development into quantum science and technology, the effect of radiation on humans, radiation emergency medicine, and the medical use of radiation.
To ensure that research and development delivers significant academic, social and economic impacts, and to maximize benefits from global innovation, QST is striving to establish world-leading research and development platforms, explore new fields, and serve as a center for radiation protection and radiation emergency medicine.
