Development of Multi-ion Radiotherapy Technology
Heavy-ions such as carbon-ions used in radiotherapy can put a large amount of energy to cell nuclei with a single collision. Linear energy transfer (LET) is a quantity that indicates its strength and strongly influences the cell killing effect. To further enhance the therapeutic effect of carbon-ion radiotherapy, we are developing a treatment planning technology called "LET painting" that actively controls LET distribution. Furthermore, although there is a limit of the LET value by LET painting, the range of LET is greatly expanded by combining beams of multiple ion species (multi-ions). It enables heavy-ion radiotherapy that optimizes not only the dose distribution but also the LET distribution.
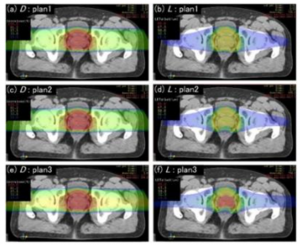
Dose distribution chart (a, c, e) and LET distribution chart (b, d, f) of three cases of multi-ion radiotherapy for prostate cancer. The plan1 sets the target LET to 50 keV/mm. The plan2 further sets the rectal LET to <30 keV/mm. The plan3 further sets the prostate LET to 80 keV/mm.
Member

Inaniwa Taku Group Leader
- Tanaka Sodai Principal Researcher
- Kasamatsu Koki Researcher
- Masuda Takamitsu Researcher
- Koike Aki Technical Staff
Selected Publications
- Masuda T., Koto M., Ikawa H., Takei H., Aoki K., Nakaji T., Inaniwa T.: Design of multi-ion therapy for Head and Neck cancers using carbon-, oxygen-, and neon-ion beams: potential efficacy against tumor hypoxia. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 70, 085003, (2025)
- Inaniwa T., Masuda T., Kanematsu N.: Effects of intra-tumoral cellular heterogeneity of oxygen partial pressure on biological effectiveness of hydrogen-, helium-, carbon-, oxygen-, and neon-ion beams. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 70 (2025)
- Tanaka S,Inaniwa T.:Method for fabricating a mesh ripple filter for charged-particle therapy.Physics in Medicine and Biology,69,145009,(2024)
- Inaniwa T.,Kanematsu N.,Koto M.: Biological dose optimization incorporating intra-tumoral cellular radiosensitivity heterogeneity in ion-beam therapy treatment planning. Physics in Medicine and Biology,69,115017,(2024)
- Inaniwa T.,Kanematsu N.,Nakajima M.: Modeling of the resensitization effect on carbon-ion radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Physics in Medicine and Biology,69,105015,(2024)
- Tanaka S.,Nakaji T.,Mizuno H.,Mizushima K.,Katagiri K.,Kasamatsu K.,Masuda T., Inaniwa T.:Safety analysis using event tree analysis for multi-ion therapy.Japanese Journal of Medical Physics,44,1-7,(2024)
- Masuda T.,Inaniwa T.:Effects of cellular radioresponse on therapeutic helium-, carbon-,oxygen-,and neon-ion beams:a simulation study.Physics in Medicine and Biology,69,045003,(2024)
- Inaniwa T.,Kanematsu N.:Event-by-event approach to the oxygen-effect-incorporated stochastic microdosimetric kinetic model for hypofractionated multi-ion therapy.Journal of Radiation Research,64,685-692,(2023)
- Inaniwa T.,Weichert E.,Masuda T.,Tanaka S.,Matsufuji N.,Kanemastu N.: Stopping-power ratio of body tissues with updated effective energies and elemental I values for treatment planning of proton therapy and ion beam therapy with helium,carbon,oxygen,and neon ions.Radiological Physics and Technology,16,319-324,(2023)
- Tanaka S.,Inaniwa T.,Matsuba S.:Development of ripple filter composed of metal mesh for charged-particle therapy.Physics in Medicine and Biology,67,13NT01,(2022)
