Industry-Academia Collaboration at QST
Our agency (QST) conducts research and development on quantum science and technology, the effects of radiation on the human body, radiation medicine, and radiation with the aim of improving the level of science and technology such as research and development related to medical use, we will collaborate with domestic and overseas research institutes, universities, and industry. We promote personnel exchange, conduct comprehensive research and development related to quantum science and technology, and carry out activities to return the results to society.
Promotion of Joint Research
By conducting joint research on common issues on an equal footing with researchers from external institutions such as private companies, universities, and public research institutes, we will actively promote joint research in order to create excellent research results and return the obtained research results to society.
Tax Credit System for Special Trials and Research Associated with Joint Research and Contract Research
If a company conducts joint research or contract research with QST, it can take advantage of the "Special Research Expense Tax Credit System".
For information on how to use the system, please refer to the "Manual for Determining the Amount of Special Testing and Research Expenses". The format of the certification application form is as follows: Please obtain it from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry's website "Report Form and Application Form for the Special Test and Research Expense Tax Credit System" (in Japanese only).
* If you are planning to receive certification for the amount of special examination and research expenses, please check the above manual and Please consult with us before concluding a contract.
Joint Research under the Collaborative Priority Research Program
With the aim of efficiently promoting basic research activities that will serve as the foundation for future creative science and technology, QST and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency Japan This is a system in which the Department of Nuclear Energy, Graduate School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo, conducts joint research.
(In some cases, institutions other than the above three parties may participate in joint research.)
Consultation Desk for Rules on the Use of Public Research Funds
In the case of accepting research funds related to joint research, contract research, etc. from the Institute, etc., rules regarding the use of public research funds and we have set up the following contact point to receive consultations on administrative procedures.
Research Collaboration Promoting Section, Department of Innovation Strategy
Tel:+81-43-206-3146,3023 Fax:+81-43-206-4061
E-mail:innov-prom1@qst.go.jp
Promoting the Practical Application of Intellectual Property
Practical application of intellectual property rights and know-how such as patents held by the Organization by industry, contract testing using the technologies owned by the Organization, we promote the implementation of technical guidance.
Patent Database
Patents published and registered after 2023 are listed. (including patents shared with other organizations)
* The gazettes posted in this database are patent information platforms operated by the Industrial Property Information and Training Center. (J-Platpat).
Heavy ion radiotherapy and accelerators, radiopharmaceuticals and diagnostic imaging, genes and organisms, environmental measurement, environmental and protection, and others it is also possible to take a look.
Patent Database (partially in Japanese)
Examples of Practical Applications of Intellectual Property
The Institute manages research results as intellectual property and promotes their practical application. Here are some examples of research results that are being returned to society in the form of products.
Pbb3 to image tau protein accumulation
Patent License
 NARD Research Institute, Inc. has commercialized a PET imaging agent developed by NIRS that uses a compound (Pbb3) that accumulates in tau protein, which is directly linked to neuronal death in dementia. This makes it possible to make a differential diagnosis of dementia from the early stages of the disease and to objectively evaluate the degree of progression of the disease. In addition, Pbb3 is expected to contribute to the development of fundamental treatments for dementia, such as the evaluation of tau accumulation suppression drugs using mouse models, and the subsequent evaluation of new therapeutic agents in humans.
NARD Research Institute, Inc. has commercialized a PET imaging agent developed by NIRS that uses a compound (Pbb3) that accumulates in tau protein, which is directly linked to neuronal death in dementia. This makes it possible to make a differential diagnosis of dementia from the early stages of the disease and to objectively evaluate the degree of progression of the disease. In addition, Pbb3 is expected to contribute to the development of fundamental treatments for dementia, such as the evaluation of tau accumulation suppression drugs using mouse models, and the subsequent evaluation of new therapeutic agents in humans.
Trace Plasma Radioactivity Concentration Measurement System "μFmpc"
Joint Research →Patent License

CD-Well
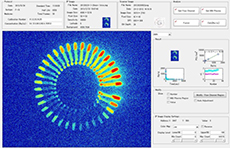
Analysis software
As a result of joint research between Shimadzu Corporation and NIRS, we have commercialized the microplasma radioactivity concentration measurement system "μFmpc", which is a tool to support pharmacokinetic analysis and pharmacodynamic evaluation in small animals such as mice using PET.
In the development of new pharmaceuticals, such as anticancer drugs and diagnostic and therapeutic agents for brain diseases, PET can be used to photograph the kinetics of the administered drugs in the body and quantitatively evaluate biological functions. However, in order to make an accurate assessment, information on changes in radioactivity concentrations in plasma over time (Tac) is required.
In the past, it was difficult to obtain data on small animals because the amount of voting per condition was as large as several tens of μL, but with this technology, the amount of voting is as small as 1~4μL, and blood can be collected at short time intervals.
This makes it possible to perform quantitative molecular imaging of PET in small animals, which is expected to promote drug discovery and the development of new treatments.
Joint research partner: Shimadzu Corporation
Nanoparticle MRI contrast agent
Joint Research →Patent License
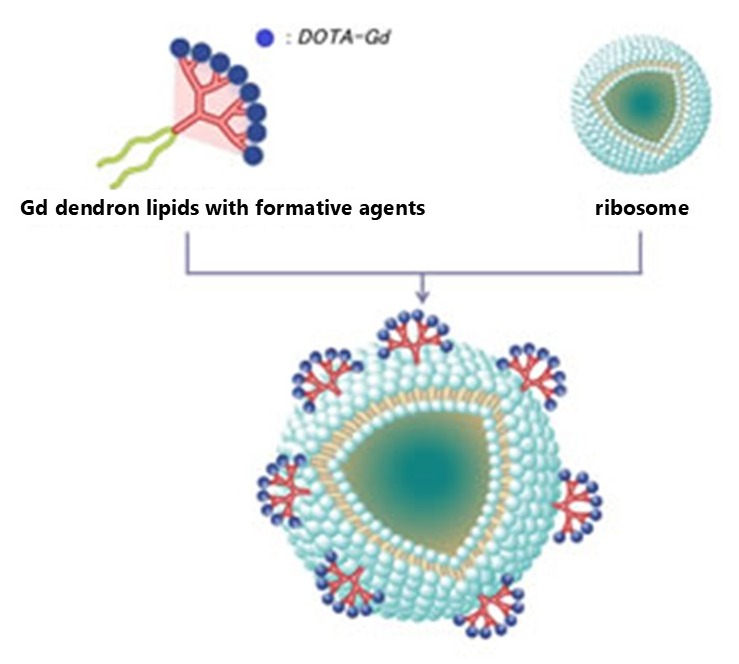
We have developed an elemental technology for incorporating dendron lipids into liposomes, which is the result of joint research by Osaka Prefecture University and NIRS, and have commercialized nanoparticle-type MRI angiography agents and reagents with excellent contrast effects.
Conventional contrast media are made up of small molecules called one complex, and each contrast agent is encased in a single complex (particle).
With this new technology, a large number of contrast agents were incorporated into the surface of the liposome, which is a nanometer-sized particle (nanoparticle), by incorporating a large number of compounds (dendron lipids) that can bind a large number of contrast agents to the surface of the liposome.
Since the number of contrast agents per particle is large, it is possible to observe with MRI with a much higher sensitivity than conventional particles, and as a result, it has led to the realization of a resolution approaching that of a microscope of 50 microns or less. In addition, it is possible to apply tumor detection imaging using the accumulation of cancer and "treatment while diagnosing" (theranostics) by installing anticancer drugs.
Joint research partner: Osaka Prefecture University
High-speed hotspot monitor R-eye
Joint Research →Patent License
 We have further developed a predictive response radiation detector, which is the result of joint research with Amano Research Institute, Inc., and in joint research with Applied Photonics Research Institute, Inc., we have commercialized a high-speed hotspot monitor that can predict the amount of radiation (counting rate) at a speed of 30 times faster than conventional portable radiation survey meters.
We have further developed a predictive response radiation detector, which is the result of joint research with Amano Research Institute, Inc., and in joint research with Applied Photonics Research Institute, Inc., we have commercialized a high-speed hotspot monitor that can predict the amount of radiation (counting rate) at a speed of 30 times faster than conventional portable radiation survey meters.
The Predictive Response function is a function that allows you to predict the counting rate from hot spots in a short time and efficiently measure a wide area.
This high speed can be used in the following ways.
- Assessing the degree of contamination before and after decontamination work in Fukushima
- Periodic confirmation of contamination in the gardens of each household after decontamination
- Periodic contamination inspections at radiation facilities, etc.
Joint research partners: Amano Research Institute, Inc., Applied Photonics Research Institute, Inc.
Direction-finding monitoring post
Japan Science and Technology Agency: Joint research through "contract development" of creative seed development project → patents and know-how license
 Conventional monitoring posts for detecting leaks of radioactive materials and radiation from nuclear power plants only measure air dose rates.
Conventional monitoring posts for detecting leaks of radioactive materials and radiation from nuclear power plants only measure air dose rates.
In addition to the air dose rate, this device can measure and indicate the direction of radiation flight, and when a high dose rate is indicated, it is possible to judge whether the radiation is caused by a nuclear power plant or a natural cause from the direction of radiation.
This device has been installed at the radiation monitoring center of a nuclear power plant in Japan, and recently the development of a hotspot probe device in Fukushima using this technology is underway.
Joint research partner: Hitachi Aloka Medical Co., Ltd.
Related Links
- Public Releases (in Japanese only)
- Institute for Radiological Science Research Activities
- Research Data Policy [PDF/152KB] (in Japanese only)
Technology Transfer and Technical Guidance
We provide technical guidance for contract testing (testing, analysis, measurement, analysis, evaluation, etc.) using the technology possessed by the Institute. If you are interested, please contact the Research Collaboration Promoting Section, Department of Innovation Strategy.
