CREATION
New Functional Materials can be created using Ion Beams.
Highly functional memberanes
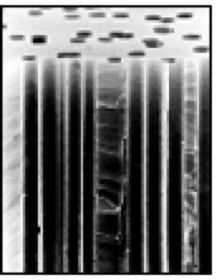 Heavy ions with high linear energy transfer (LET) can produce cylindrical nanopores with an extremely high aspect ratio in polymeric membranes; the diameter of the pores ranges from 0.01μm to 1μm which is one-ten thousandth of the thickness of a membrane.
Heavy ions with high linear energy transfer (LET) can produce cylindrical nanopores with an extremely high aspect ratio in polymeric membranes; the diameter of the pores ranges from 0.01μm to 1μm which is one-ten thousandth of the thickness of a membrane.
Such nanopores cannot be produced with other existing techniques like photolithography or laser processing.
How is it produced?
A polymeric membrane irradiated with high-energy heavy ions may have ion tracks through the membrane, where the material is damaged. These latent ion-tracks can be selectively dissolved with a chemical regent, and hence nanopores are produced. The inner diameter can be changed by controlling the conditions of the chemical treatment.
What's possible?
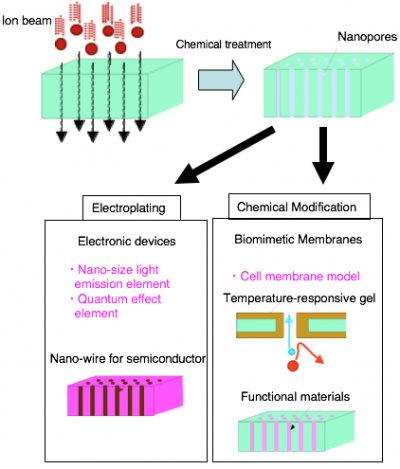
The inner surfaces of the cylindrical pores can be modified by applying radiation-induced graft polymerization. For example, temperature- and pH-responsive gels can be formed there. This pore enables open-close control according to slightest environmental change. Membranes with such functional pores are expected to perform selective separation of proteins and useful substances.
High efficiency photocatalytic thin-film
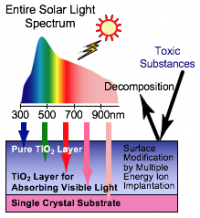
 Ion implantation is used together with laser ablation to produce the high efficiency photocatalytic materials that decompose toxic substances with visible light. When light is absorbed by titanium dioxide, electrons and holes are produced. The holes move to the surface of the materials and decompose the adsorbed substances. This phenomenon is called the photocatalytic reaction. Titanium dioxide shows its photocatalytic effect only when irradiated by short-wavelength light, such as ultraviolet rays. This makes it highly important to improve the reaction efficiency. Ion implantation following laser ablation thin-film synthesis resolves this problem.
Ion implantation is used together with laser ablation to produce the high efficiency photocatalytic materials that decompose toxic substances with visible light. When light is absorbed by titanium dioxide, electrons and holes are produced. The holes move to the surface of the materials and decompose the adsorbed substances. This phenomenon is called the photocatalytic reaction. Titanium dioxide shows its photocatalytic effect only when irradiated by short-wavelength light, such as ultraviolet rays. This makes it highly important to improve the reaction efficiency. Ion implantation following laser ablation thin-film synthesis resolves this problem.
How is it created?
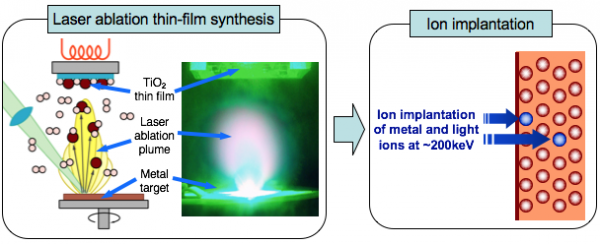
TiO2 thin-film with atomic ordered structure is produced by laser ablation method.
Ions are doped to TiO2 to improve the photocatalytic reaction efficiency by raising its sensitivity to visible light.
What's possible?
Various toxic substances in the environment can be removed efficiently by photocatalytic function of the material, through the decomposition using infinite solar light. For instance, the toxic substances spewed from automobiles can be purged if a protective highway wall is made of the phtocatalytic materials.
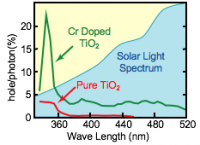
TiO2 doped with Cr ions as an example of a transition-metal element has high sensitivity not only to ultraviolet light but also to visible light.