Ion irradiation research facility
 Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) is an ion irradiation facility designed to utilize the features of ion beams for research on advanced science such as material science and biotechnology, which is placed in Takasaki Institute for Advanced Quantum Science. The facility consists of following four accelerators; an AVF Cyclotron, a Tandem Accelerator, a Single Ended Accelerator and an Ion Implanter. It was constructed in July 1993 and was fully in operation from January 1994.
Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) is an ion irradiation facility designed to utilize the features of ion beams for research on advanced science such as material science and biotechnology, which is placed in Takasaki Institute for Advanced Quantum Science. The facility consists of following four accelerators; an AVF Cyclotron, a Tandem Accelerator, a Single Ended Accelerator and an Ion Implanter. It was constructed in July 1993 and was fully in operation from January 1994.
The photo on the right shows the emission of the hydrogen plasma in the RF ion source mounted on the single-ended accelerator.
Gamma-ray (60Co) irradiation facilities
 The 60Co first irradiation building, the second irradiation building, and the food irradiation building store a large amount of 60Co gamma-ray sources in deep water pools for shielding. The radiation sources are raised from the pool into an irradiation room for irradiation. The irradiation rooms are surrounded by heavy concrete walls with a thickness of 1.3 m. The 1st, the 2nd, and the food irradiation building have three, three, and two irradiation rooms, respectively.
The 60Co first irradiation building, the second irradiation building, and the food irradiation building store a large amount of 60Co gamma-ray sources in deep water pools for shielding. The radiation sources are raised from the pool into an irradiation room for irradiation. The irradiation rooms are surrounded by heavy concrete walls with a thickness of 1.3 m. The 1st, the 2nd, and the food irradiation building have three, three, and two irradiation rooms, respectively.
The picture on the right shows Cherenkov radiation from cobalt-60 sources in water.
Electron beam irradiation facility
 The electron accelerator consists of a high voltage generator and an acceleration tube. The electrons are generated from the electron gun with the tungsten filament mounted on the high voltage terminal, and accelerated to the ground potential through the vacuum tube by an electric field. They are extracted from the vacuum tube into the air through titanium window. The electron accelerator, equipped with two acceleration tubes, has a dual beam system, supplying either a vertical or a horizontal electron beam.
The electron accelerator consists of a high voltage generator and an acceleration tube. The electrons are generated from the electron gun with the tungsten filament mounted on the high voltage terminal, and accelerated to the ground potential through the vacuum tube by an electric field. They are extracted from the vacuum tube into the air through titanium window. The electron accelerator, equipped with two acceleration tubes, has a dual beam system, supplying either a vertical or a horizontal electron beam.
The electrons accelerated downwards are scanned by a magnetic field. Uniform irradiation over 120 cm wide is available in the vertical beam irradiation room. The methods of irradiation are stationary and conveyor.
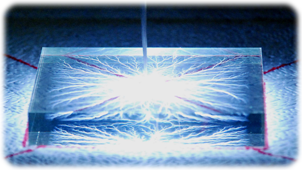
The right-hand picture shows the view of the electron tree creation using the accelerator. The excess negative charge implanted to an acrylic target by the accelerator is discharged and the electrons escape with a bright flash and loud bang. The hot, lightning-like discharges create a fractal pattern of fractures inside the acrylic resulting in an overall branching "Frozen Lightning" sculpture (Lichtenberg Figure).
