Radiative divertor plasma coexisted with improved confinement in the reversed shear plasma
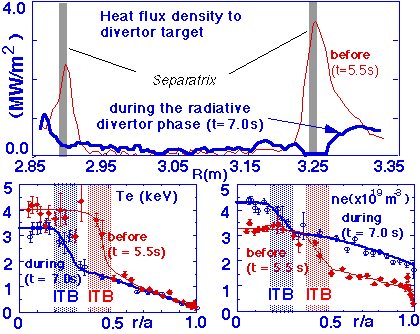
Radiative divertor study is an urgent issue for ITER physics R & D. The radiative divertor protects the divertor target like a cushion against heat flux in which a large fraction of heat flux from the main plasma is lost through radiative energy from the dense and cold plasmas. It has been demonstrated in JT-60U for the first time that the radiative divertor plasma can be sustained with improved confinement inside the internal transport barrier (ITB) in the reversed shear plasmas. The reversed shear plasma is a promising operation mode for a steady state tokamak reactor.
Controlled neon and hydrogen gas puff was applied to the reversed shear plasma with the ITB. A radiative divertor plasma was successfully formed and 70% of heat flux from the main plasma was dissipated in the divertor plasma. While the radius of the ITB shrunk with time due to the relaxation of the current profile, the ITB was sustained with the radiative divertor.