Highest Current Drive Efficiency with Negative-Ion Based NBI
For continuous operation of a nuclear fusion reactor, efficient current drive by the use of NBI or RF waves is essential. In order to increase the current drive efficiency with NBI, both higher beam energy and electron temperature are simultaneously required.
In JT-60U, a negative-ion based NBI (N-NBI) has been installed and operated to increase the current drive efficiency since the N-NBI is a most promising current driver in ITER. Recently, JT-60U achieved the world highest current-drive efficiency of 1.6x1019 A/W/m2 for N-NBI at 360 keV under high electron temperature (160x106 kelvin) approaching the ITER relevant regime (see figure bellow). Such high temperature was accomplished with additional electron cyclotron heating (110 GHz, 1.5 MW). In this parameter regime, measured driven currents agree well with calculated values. The achieved efficiency is three times higher than that obtained by conventional positive-ion based NBI (P-NBI) with 85 keV.
This result provides the prospect for achieving high current-drive efficiency required for ITER and significantly contributes to the development of a fusion reactor.
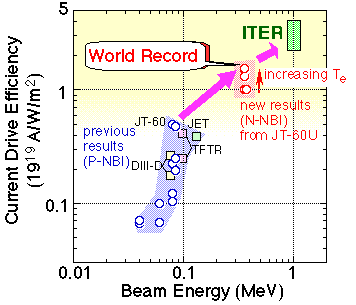
Fig. World highest current-drive efficiency 1.6x1019 A/W/m2 was achieved by the use of N-NBI. The achieved value is three times better than that by P-NBI.
