High Power and Long Pulse Operation of Negative-Ion based NBI in JT-60U
High energy neutral beam injection into a plasma is widely considered necessary to heat plasmas and generate plasma current in the tokamak fusion reactors. Since the negative ions are converted into neutral particles more efficiently than the positive ions, the development of the negative-ion based neutral particle beam injection (N-NBI) system is an important issue. In JT-60U the convergence of the negative-ion based neutral beam was lower than predicted so that the peripheral beams caused the overheat of the injection port.
A new method to enable the fine adjustment of the beam trajectory for the ion source has been applied so that the beam convergence performance was improved up to 20% better than the previous one. This has allowed the beam to be injected into the plasma without the overheat of the injection port leading to a significant improvement in the performance of the N-NBI system. As a result, a high energy (360 keV) and high power (2.6 MW) neutral beam was successfully injected for 10 seconds in JT-60U as shown in Fig.1. It was found that major components of the N-NBI system including the negative ion sources, reached a thermally steady state in about 8 seconds. This means an important technical accomplishment for continuous injection of a negative-ion based neutral particle beam in the fusion reactors.
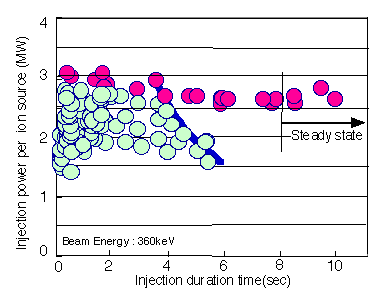
Fig. 1 Performance of injection power and duration of the N-NBI in JT-60U. 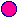 indicates the results of improved beam convergence and
indicates the results of improved beam convergence and 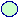 previous results. The blue solid line shows the previous limit of the injection power and duration.
previous results. The blue solid line shows the previous limit of the injection power and duration.
