Abstract
The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect is variable depending on nanoparticleproperties and tumor/vessel conditions. Thus, intratumoral evaluations of the vasculature and nanoparticle distribution are important for predicting the therapeutic efficacy and the intractability of tumors. We aimed to develop a tumor vasculature evaluation method and high-resolution nanoparticle delivery imaging using magnetic resonance (MR) micro-imaging technology with a gadolinium (Gd)-dendron assembled liposomal contrast agent. Using the Gd-liposome and a cryogenic receiving coil, we achieved 50-μm isotropic MR angiography with clear visualization of tumor micro-vessel structure. The Gd-liposome-enhanced MR micro-imaging revealed differences in the vascular structures between Colon26- and SU-DHL6-grafted mice models. The vessel volumes and diameters measured for both tumors were significantly correlated with histological observations. The MR micro-imaging methods facilitate the evaluation of intratumoral vascularization patterns, the quantitative assessment of vascular-properties that alter tumor malignancy, particle retentivity, and the effects of treatment.
Image
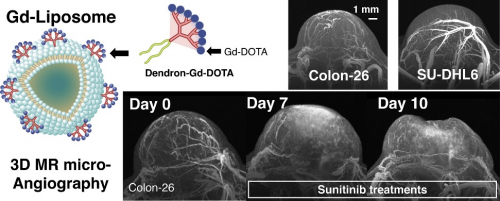
The Gd-liposome with a cryogenic RF coil achieved 50-μm isotropic MR angiography with clear visualization of tumor micro-vessel structure and revealed differences in the vascular structures between Colon26- and SU-DHL6-tumor models.
Reference
Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine
Intratumoral evaluation of 3D microvasculature and nanoparticle distribution using a gadolinium-dendron modified nano-liposomal contrast agent with magnetic resonance micro-imaging
Nobuhiro Nitta,1,2,3 Yoichi Takakusagi,1,2 Daisuke Kokuryo,4 Sayaka Shibata,1,2 Akihiro Tomita,5 Tatsuya Higashi,1 Ichio Aoki,1,2*, Masafumi Harada,3
Author affiliations:
1 National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS), National Institutes of Radiological Science and Technology (QST), 4-9-1 Anagawa, Inage, Chiba, 263-8555, Japan.
2 Group of Quantum-state Controlled MRI, QST, 4-9-1 Anagawa, Inage, Chiba, 263-8555, Japan.
3 Graduate School of Medicine, Tokushima University, 3-18-15, Kuramoto-cho, Tokushima 770-8503, Japan.
4 Graduate School of System Informatics, Kobe University, 1-1, Rokkodai-cho, Nada-ku, Kobe, Hyogo, 657-8501, Japan
5 Department of Hematology, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, 1-98 Dengakugakubo, Kutsukake-cho, Toyoake, Aichi, 470-1192, Japan
*Corresponding Author
Contact
Ichio Aoki (fmit3=qst.go.jp) (replace"="with"@")
Department of Molecular Imaging and Theranostics,National Institute of Radiological Sciences, QST
