Short-Lived Radioisotope 98Tc Synthesized by the Supernova Neutrino Process
Posted on 2018年9月6日
Short-Lived Radioisotope 98Tc Synthesized by the Supernova Neutrino Process
Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 102701 – Published 4 September 2018
The isotope 98Tc decays to 98Ru with a half-life of 4.2×106 yr and could have been present in the early Solar System. In this Letter, we report on the first calculations of the production of 98Tc by neutrino-induced reactions in core-collapse supernovae (the ν process). Our predicted 98Tc abundance at the time of solar system formation is not much lower than the current measured upper limit raising the possibility for its detection in the not too distant future. We show that, if the initial abundance were to be precisely measured, the 98Tc nuclear cosmochronometer could be used to evaluate a much more precise value of the duration time from the last core-collapse supernova to the formation of the solar system. Moreover, a unique and novel feature of the 98Tc ν-process nucleosynthesis is the large contribution (∼20%) from charged current reactions with electron antineutrinos. This means that 98Tc becomes a unique new ν-process probe of the temperature of the electron antineutrinos.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.102701
Properties of the RF transmission line of a C-shaped waveguide
Posted on 2017年11月27日 by lcs
Properties of the RF transmission line of a C-shaped waveguide
Masaru Sawamura, Masato Egi, Kazuhiro Enami, Takaaki Furuya, Hiroshi Sakai, KenseiUmemori
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment
Volume 882, 21 February 2018, Pages 30-40
Abstract
A new type of waveguide, named the C-shaped waveguide (CSWG), has a structure similar to that of a coaxial line but with a plate connecting the inner conductor to the outer conductor. The CSWG has unique characteristics, such as a cutoff frequency and easy cooling of the inner conductor, that are absent in the coaxial line. The results of calculations using 3-dimensional simulation software and measurement with the CSWG model are in good agreement with the analytical solution. The CSWG can be applied to a pickup port with a high-pass filter that can attenuate the higher-order modes over the cutoff frequency without attenuating the accelerating mode.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2017.09.067
published manuscript (free download for 50 days) PDF
accepted manuscript: PDF
Generating Carrier-Envelope-Phase Stabilized Few-Cycle Pulses from a Free-Electron Laser Oscillator
Posted on 2017年11月20日
Generating Carrier-Envelope-Phase Stabilized Few-Cycle Pulses from a Free-Electron Laser Oscillator
Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 204802 – Published 15 November 2017
We propose a scheme to generate carrier-envelope-phase (CEP) stabilized few-cycle optical pulses from a free-electron laser oscillator. The CEP stabilization is realized by the continuous injection of CEP-stabilized seed pulses from an external laser to the free-electron laser oscillator whose cavity length is perfectly synchronized to the electron bunch repetition. Operated at a midinfrared wavelength, the proposed method is able to drive a photon source based on high harmonic generation (HHG) to explore the generation of isolated attosecond pulses at photon energies above 1 keV with a repetition of >10 MHz. The HHG photon source will open a door to full-scale experiments of attosecond x-ray pulses and push ultrafast laser science to the zeptosecond regime.
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.204802
Low-lying dipole strength in 52Cr
Posted on 2017年10月27日
Low-lying dipole strength in 52Cr
Phys. Rev. C 96, 044316 – Published 13 October 2017
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.96.044316
Construction and commissioning of the compact energy-recovery linac at KEKs
Posted on 2017年10月19日
Construction and commissioning of the compact energy-recovery linac at KEKs
Mitsuo Akemoto, DaiArakawa, Seiji Asaoka, Enrico Cenni, Masato Egi,
Kazuhiro Enami, Kuninori Endo, Shigeki Fukuda, Takaaki Furuya, Kaiichi Haga,
Ryoichi Hajima, Kazufumi Hara, Kentaro Harada, Tohru Honda, Yosuke Honda,
Teruya Honma, Kenji Hosoyama, Eiji Kako, Hiroaki Katagiri, Hiroshi Kawata,
Yukinori Kobayashi, Yuuji Kojima, Yoshinari Kondou, Olga Tanaka,
Tatsuya Kume, Masao Kuriki, Hiroshi Matsumura, Hideki Matsushita,
Shinichiro Michizono, Takako Miura, Tsukasa Miyajima, Shinya Nagahashi,
Ryoji Nagai, Hirotaka Nakai, Hiromitsu Nakajima, Norio Nakamura,
Kota Nakanishi, Kazuyuki Nigorikawa, Nobuyuki Nishimori,
Takashi Nogami, Shuichi Noguchi, Takashi Obina, Feng Qiu, Hidenori Sagehashi,
Hiroshi Sakai, Shogo Sakanaka, Shinichi Sasaki, Kotaro Satoh, Masaru Sawamura,
Miho Shimada, Kenji Shinoe, Toshio Shishido, Mikito Tadano, Takeshi Takahashi,
Ryota Takai, Tateru Takenaka, Yasunori Tanimoto, Takashi Uchiyama,
Akira Ueda, Kensei Umemori, Ken Watanabe, MasahiroYamamoto
Nuclear Instruments and Physics Research A Volume 877, 1 January 2018, Pages 197-219 DOI: 10.1016/j.nima.2017.08.051
accepted manuscript PDF published manuscript (free download until Dec. 5, 2017) PDF
Energy-recovery linacs (ERLs) are promising for advanced synchrotron light sources, high-power free electron lasers (FELs), high-brightness gamma-ray sources, and electron–ion colliders. To demonstrate the critical technology of ERL-based light sources, we have designed and constructed a test accelerator, the compact ERL (cERL). Using advanced technology that includes a photocathode direct current (DC) electron gun and two types of 1.3-GHz-frequency superconducting cavities, the cERL was designed to be capable of recirculating low emittance (1 mm mrad) and high average-current (10 mA) electron beams while recovering the beam energy. During initial commissioning, the cERL demonstrated successful recirculation of high-quality beams with normalized transverse emittance of 0.14 mm mrad and momentum spread of 1.2 10−4 (rms) at a beam energy of 20 MeV and bunch charge below 100 fC. Energy recovery in the superconducting main linac was also demonstrated for high-average-current continuous-wave beams. These results constitute an important milestone toward realizing ERL-based light sources.
Nondestructive Inspection System for Special Nuclear Material
Posted on 2017年7月19日
Nondestructive Inspection System for Special Nuclear Material Using Inertial Electrostatic Confinement Fusion Neutrons and Laser Compton Scattering Gamma-Rays
H. Ohgaki, I. Daito, H. Zen, T. Kii, K. Masuda, T. Misawa, R. Hajima, T. Hayakawa, T. Shizuma, M. Kando, S. Fujimoto
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science ( Volume: 64, Issue: 7, July 2017 )
Page(s): 1635 – 1640
Date of Publication: 16 January 2017
DOI: 10.1109/TNS.2017.2652619 — accepted manuscript
A Neutron/Gamma-ray combined inspection system for hidden special nuclear materials (SNMs) in cargo containers has been developed under a program of Japan Science and Technology Agency in Japan. This inspection system consists of an active neutron-detection system for fast screening and a laser Compton backscattering gamma-ray source in coupling with nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) method for precise inspection. The inertial electrostatic confinement fusion device has been adopted as a neutron source and two neutron-detection methods, delayed neutron noise analysis method and high-energy neutron-detection method, have been developed to realize the fast screening system. The prototype system has been constructed and tested in the Reactor Research Institute, Kyoto University. For the generation of the laser Compton backscattering gamma-ray beam, a race track microtron accelerator has been used to reduce the size of the system. For the NRF measurement, an array of LaBr3(Ce) scintillation detectors has been adopted to realize a low-cost detection system. The prototype of the gamma-ray system has been demonstrated in the Kansai Photon Science Institute, National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology. By using numerical simulations based on the data taken from these prototype systems and the inspection-flow, the system designed by this program can detect 1 kg of highly enriched 235U (HEU) hidden in an empty 20-ft container within several minutes.
Including Delbrück scattering in GEANT4
Posted on 2017年5月24日
Including Delbrück scattering in GEANT4
Mohamed Omer and Ryoichi Hajima
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms Volume 405, 15 August 2017, Pages 43–49
DOI:10.1016/j.nimb.2017.05.028
Free Download until 12, July 2017.
Related link: Possible Precise Measurement of Delbrück Scattering Using Polarized Photon Beams
Possible Precise Measurement of Delbrück Scattering Using Polarized Photon Beams
Posted on 2017年5月18日
Possible Precise Measurement of Delbrück Scattering Using Polarized Photon Beams
Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 204801 – Published 17 May 2017
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.204801
published paper PDF: PhysRevLett.118.204801
High voltage threshold for stable operation in a dc electron gun
Posted on 2016年7月11日
High voltage threshold for stable operation in a dc electron gun
M. Yamamoto and N. Nishimori
Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 014103 (2016)
We report clear observation of a high voltage (HV) threshold for stable operation in a dc electron gun. The HV hold-off time without any discharge is longer than many hours for operation below the threshold, while it is roughly 10 min above the threshold. The HV threshold corresponds to the minimum voltage where discharge ceases. The threshold increases with the number of discharges during HV conditioning of the gun. Above the threshold, the amount of gas desorption per discharge increases linearly with the voltage difference from the threshold. The present experimental observations can be explained by an avalanche discharge model based on the interplay between electron stimulated desorption (ESD) from the anode surface and subsequent secondary electron emission from the cathode by the impact of ionic components of the ESD molecules or atoms.
Journal web page: DOI:/10.1063/1.4955180
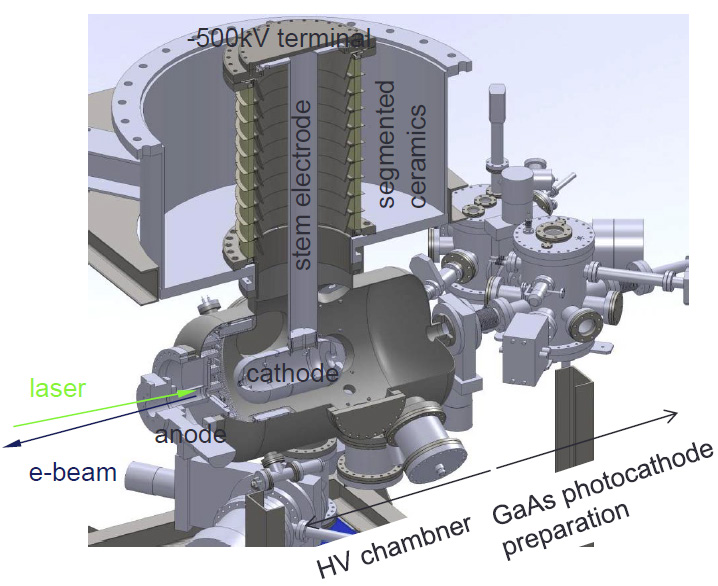
A 500-kV DC photocathode gun developed by our group
Simple synchronization technique of a mode-locked laser for Laser-Compton scattering γ-ray source
Posted on 2016年7月1日
Simple synchronization technique of a mode-locked laser for Laser-Compton scattering γ-ray source
Michiaki Mori, Atsushi Kosuge, Hiromitsu Kiriyama, Ryoichi Hajima and Kiminori Kondo
Review of Scientific Instruments 87, 063307 (2016)
Abstract
We propose a simple and effective synchronization technique between a reference electrical oscillator and a mode-locked laser for a narrowband picosecond Laser-Compton scattering γ-ray source by using a commercial-based 1-chip frequency synthesizer, which is widely used in radio communication. The mode-locked laser has been successfully synchronized in time with a jitter of 180 fs RMS for 10 Hz–100 kHz bandwidth. A good stability of 640 μHz at 80 MHz repetition rate for 10 h operation has also been confirmed. We discuss in detail the design and performance of this technique (in terms of timing jitter, stability, and validity).
Journal site: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4954733
Accepted Manuscript: pdf_archiveRSINAKvol_87iss_6063307_1_am
