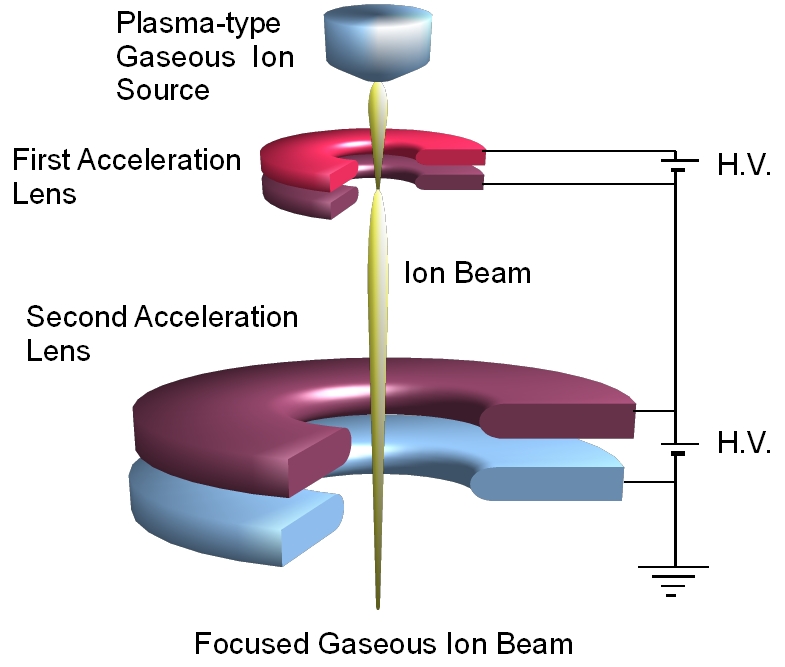
Gaseous ion nanobeam system
A focused ion beam with submicron or less in diameter (nanobeam) is generally formed by a Focused Ion Beam (FIB) system, which consists of a liquid metal ion source and conventional focusing lenses, such as magnetic quadruple lenses or einzel lens. Metal ion nanobeam, e.g. Ga+ beam, produced by FIB has the advantage of direct micromachining on the high sputtering effect and the disadvantages of destraction for analyses of microelements or of residual metal ion as impurity in a material after machining. These disadvantages are solved using gaseous ion nanobeam.
The formation of gaseous ion nanobeams using a plasama-type ion source has, so far, been difficult because a focusing lens with high demagnification which wasn't obtained by conventional focusing lenses, such as quadrupole magnets or einzel lens, was necessary. Gaseous ion nanobeam system combining the plasam-type ion source and the focusing lens system employing accelerating electric field has been developed in order to form the gaseous ion nanobeam of tens of keV. The 170 nm in diameter at 47 keV hydrogen ion beam was successfully formed using the gaseous ion nanobeam system. Furthermore the reduction of the beam size and the enhancement of beam energy has been researched in order to enlarge the application filed of the gaseous ion nanobeam.
