関西光科学研究所 >> KPSIセミナー >> Collective charged particle dynamics in relativistically transparent laser-plasma interactions
セミナー
第31回KPSIセミナー
Collective charged particle dynamics in relativistically transparent laser-plasma interactions
| 講演者 | Dr. Bruno Gonzalez izquierdo (関西光科学研究所 高強度レーザー科学研究グループ) |
|---|---|
| 職位 | 学振外国人研究員 |
| 場所 | 関西光科学研究所 ITBL棟 G201号室 |
| 日時 | 2017年11月15日(水曜日)9時30分~10時30分 |
| 使用言語 | 英語 |
| 要旨 | [PDFファイル/256KB] |
Collective charged particle dynamics in relativistically transparent laser-plasma interactions
Dr. Bruno Gonzalez izquierdo
(関西光科学研究所 高強度レーザー科学研究グループ)
概要
Significant progress has been made over the past decade in elucidating the physics of ultraintense laser pulse interactions with solid and gas targets. This has been motivated by fundamental investigations of plasma generation in extreme conditions and the development of compact laser-driven particle and radiation sources [1]. The case of ultrathin (tens-to-hundreds of nanometres) foil targets have received particular attention due to their use in the development of ion acceleration based on the radiation pressure (RPA) of the intense laser light [2]. In spite of foils, which are sufficiently thin enough to expand and undergo relativistic self-induced transparency (RSIT) [3] during the interaction, exhibit a detrimental in ion acceleration, recent studies have demonstrated that new and unsuspected phenomena arise in this regime.
My past research has been focused on experimental and numerical (via 2D-3D PIC simulations) investigations of the collective response of electrons and ions to the interaction of ultra-intense (1020 Wcm-2) laser with ultra-thin (nanometre scale) foils undergoing expansion and RSIT. Investigations of the collective response of electrons [4, 5] and protons [6] show that a “relativistic plasma aperture” is generated by intense laser light in this regime, resulting in diffraction. It was numerically found that the plasma electrons collectively respond to the produced laser near-field diffraction pattern, resulting in a beam of energetic electrons with spatial-intensity distribution, related to this diffraction structure, which can be controlled by variation of the laser pulse parameters (Figure 1). Additionally, it was shown that static electron beam structures can be made to rotate at fixed or variable angular frequencies depending on the degree of ellipticity in the laser polarisation (Figure 2). Besides, the results showed that the electron dynamics is mapped onto the beam of protons accelerated via strong charge-separation-induced electrostatic fields (Figure 3 & Figure 4).
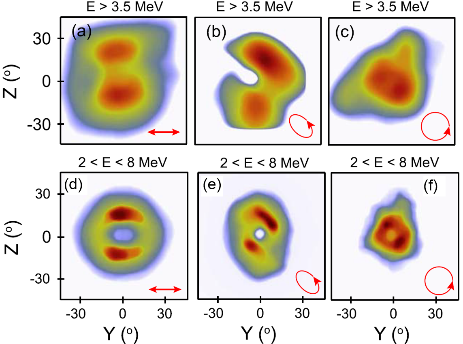
Figure 1.
Experimental electron density for (a) linear, (b) elliptical and (c) circular polarization. (d-f) Same from 3D simulation results.
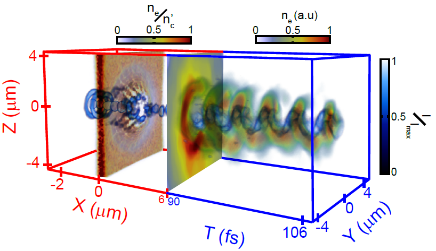
Figure 2.
Combined plot showing the 3D laser intensity profile and the temporal evolution of the electron density distribution for circular polarization.
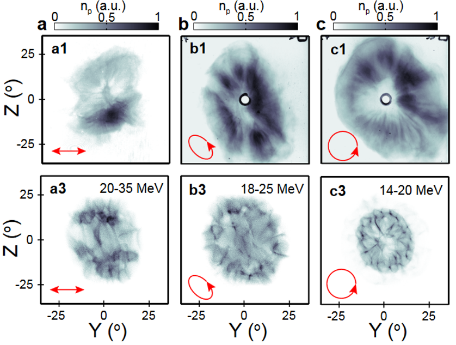
Figure 3.
Experimental proton density for (a1) linear, (b1) elliptical and (c1) circular polarization. (a3-c3) Same from 3D simulation results.
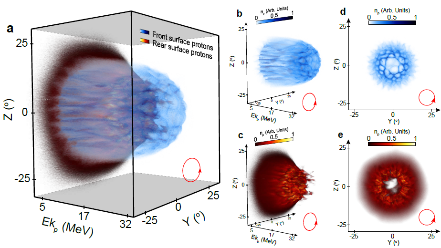
Figure 4.
(a) Combined plot showing the 3D proton density from front and rear surface. (b) and (d) Front surface protons (lateral and front view); (c) and (e) Rear surface protons.
参照:
[1] H. Daido et al., Rep. Prog. Phys., 75, 056401 (2012)
[2] T. Esirkepov et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 92, 175003 (2004)
[3] V. I. Eremin et al., Phys. Plasmas, 17, 043102 (2010)
[4] B. Gonzalez-Izquierdo et al., Nature Physics, 12, 505-512 (2016)
[5] B. Gonzalez-Izquierdo et al., HPLSE, 4, e33 (2016)
[6] B. Gonzalez-Izquierdo et al., Nature Comms., 7, 12891 (2016)
[前の記事]
第30回KPSIセミナー Short-pulse high-intensity laser-plasma science using an X-ray free electron laser
[次の記事]
第32回KPSIセミナー Relativistic electron-positron jets from intense lasers
