マルチイオン治療技術の研究開発
重粒子線がん治療で用いる炭素イオンのような重い粒子は1回の衝突で細胞核に大きなエネルギーを与えることができます。線エネルギー付与(linear energy transfer, LET)はその強さを示す量で、細胞の殺傷効果に強く影響します。重粒子線がん治療の治療効果をさらに高めるために、LETを制御する「LETペインティング」という治療計画技術を開発しています。さらに、LETペインティングでは臨床的に実現できるLETに限界がありますが、複数のイオン種のビーム(マルチイオン)を組み合わせれば制御できるLETの範囲は格段に広がり、線量分布だけでなくLET分布も最適化する重粒子線治療が可能となります。
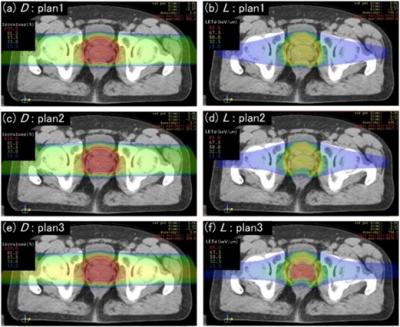
前立腺がんマルチイオン治療の3例の線量分布図(a, c, e)とLET分布図(b, d, f)
plan1は標的のLETを50 keV/ mmに設定、plan2はさらに前立腺の背側に隣接する直腸のLETを30 keV/ mm以下に制限、plan3はさらに前立腺のLETを80 keV/ mmに設定しています。
メンバー

稲庭 拓 グループリーダー
- 田中 創大 主幹研究員
- 笠松 幸生 研究員
- 増田 孝充 研究員
- 小池 亜紀 技術員
主要論文
- Masuda T., Koto M., Ikawa H., Takei H., Aoki K., Nakaji T., Inaniwa T.: Design of multi-ion therapy for Head and Neck cancers using carbon-, oxygen-, and neon-ion beams: potential efficacy against tumor hypoxia. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 70, 085003, (2025)
- Inaniwa T., Masuda T., Kanematsu N.: Effects of intra-tumoral cellular heterogeneity of oxygen partial pressure on biological effectiveness of hydrogen-, helium-, carbon-, oxygen-, and neon-ion beams. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 70 (2025)
- Tanaka S,Inaniwa T.:Method for fabricating a mesh ripple filter for charged-particle therapy.Physics in Medicine and Biology,69,145009,(2024)
- Inaniwa T.,Kanematsu N.,Koto M.: Biological dose optimization incorporating intra-tumoral cellular radiosensitivity heterogeneity in ion-beam therapy treatment planning. Physics in Medicine and Biology,69,115017,(2024)
- Inaniwa T.,Kanematsu N.,Nakajima M.: Modeling of the resensitization effect on carbon-ion radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Physics in Medicine and Biology,69,105015,(2024)
- Tanaka S.,Nakaji T.,Mizuno H.,Mizushima K.,Katagiri K.,Kasamatsu K.,Masuda T., Inaniwa T.:Safety analysis using event tree analysis for multi-ion therapy.Japanese Journal of Medical Physics,44,1-7,(2024)
- Masuda T.,Inaniwa T.:Effects of cellular radioresponse on therapeutic helium-, carbon-,oxygen-,and neon-ion beams:a simulation study.Physics in Medicine and Biology,69,045003,(2024)
- Inaniwa T.,Kanematsu N.:Event-by-event approach to the oxygen-effect-incorporated stochastic microdosimetric kinetic model for hypofractionated multi-ion therapy.Journal of Radiation Research,64,685-692,(2023)
- Inaniwa T.,Weichert E.,Masuda T.,Tanaka S.,Matsufuji N.,Kanemastu N.: Stopping-power ratio of body tissues with updated effective energies and elemental I values for treatment planning of proton therapy and ion beam therapy with helium,carbon,oxygen,and neon ions.Radiological Physics and Technology,16,319-324,(2023)
- Tanaka S.,Inaniwa T.,Matsuba S.:Development of ripple filter composed of metal mesh for charged-particle therapy.Physics in Medicine and Biology,67,13NT01,(2022)
