グループリーダー
盛武 敬
研究内容
放射線障害の克服ための新しい治療法の開発に関する研究
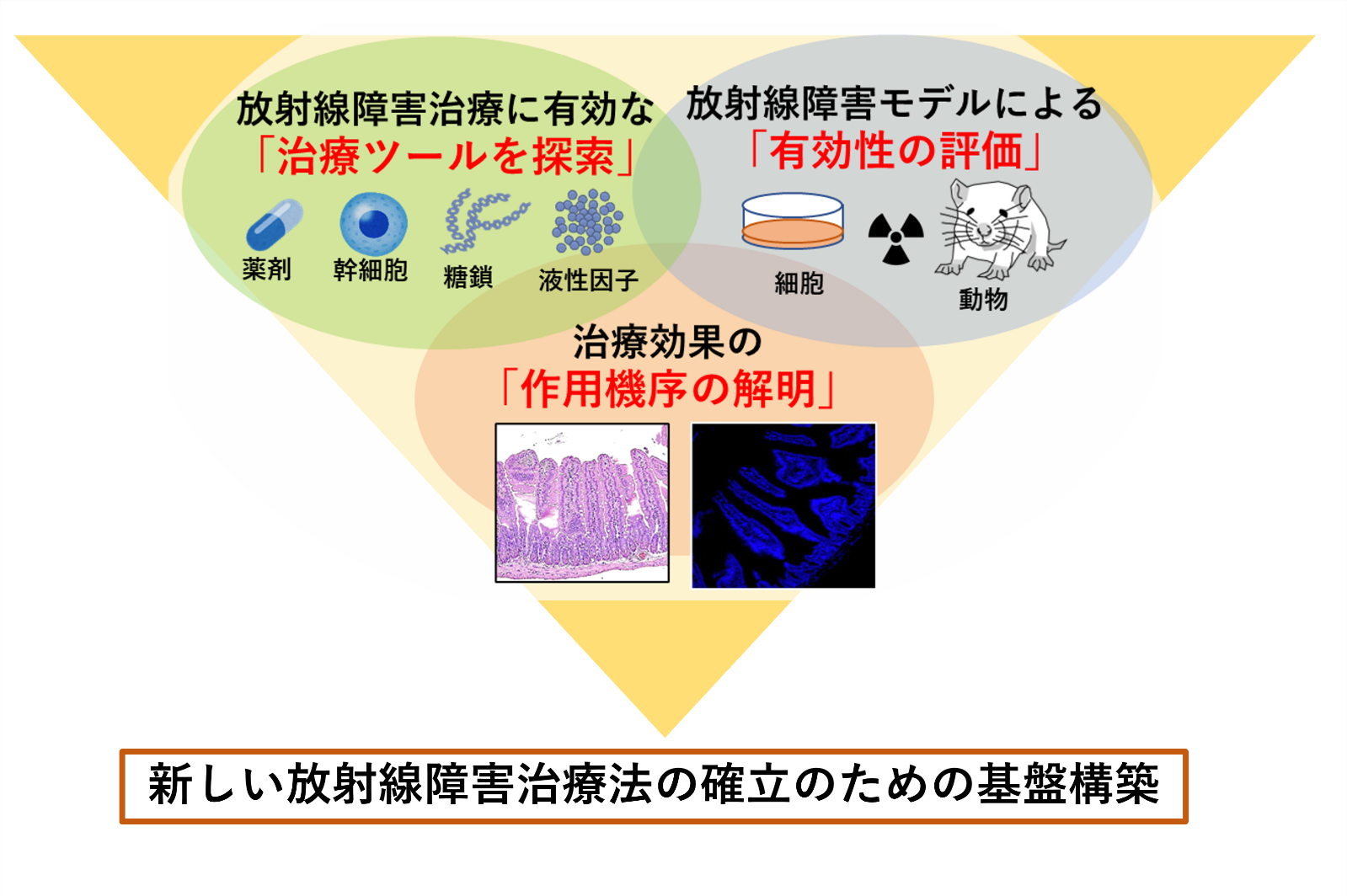
高線量被ばく事故における放射線障害及び放射線治療での毛、皮膚、消化器などの正常組織で起こる有害事象に対する予防・治療法の開発を行っています。薬剤、幹細胞、糖鎖、液性因子など、放射線障害治療に有効な治療ツールを探索・開発し、放射線障害モデルを用いて有効性を評価し、治療効果の作用機序を解明します。
さらに、探索・開発した新規治療ツールのヒトへの適用の可能についても検証し、新しい放射線障害治療法の確立のための基盤構築を目指しています。
被ばく医療への再生医療応用に向けた基礎研究
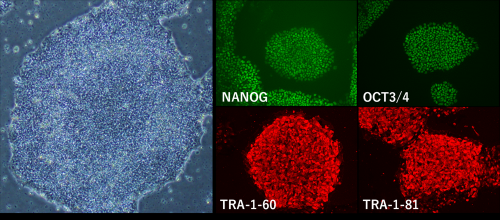
高線量放射線障害による血球減少など、組織幹細胞の障害には、幹細胞等の細胞移植、それも大量・頻回の移植を必要としますが、ドナー細胞の入手は困難なためiPS細胞等を利用した再生医療が期待されています。そこで我々は、iPS細胞生成機構を理解し、より免疫原性・腫瘍原性の低い高品質iPS細胞樹立法の研究を実施します。
List of Papers
- Miura T., Kado J., Takiyama H., Kawano M., Yamagiri A., Nishihara S., Yamada S., Nakayama F.: Stem cell therapy using bone marrow-derived Muse cells repairs radiation-induced intestinal injury through their intestine-homing via sphingosine monophosphate-sphingosine monophosphate receptor 2 interaction. Advances in Radiation Oncology. 9, 9, 101565 (2024)
- Miura T., Kado J., Ashisuke K., Masuzawa M., Nakayama F.: Sustained activation of the FGF1-MEK-ERK pathway inhibits proliferation, invasion and migration and enhances radiosensitivity in mouse angiosarcoma cells. Journal of Radiation Research. 65, 3, 303-314 (2024)
- Araki R., Suga T., Hoki Y., Imadome K., Sunayama M., Kamimura S., Fujita M., Abe M.: iPS cell generation-associated point mutations include a significant number of C>T substitutions as a result of different cytosine modification mechanisms. Nat Commun. 15, 4946 (2024)
- Miura T., Kawano M., Takahashi K., Yuasa N., Habu M., Kimura F., Imamura T., Nakayama F.: High-sulfated hyaluronic acid ameliorates radiation-induced intestinal damage without blood anticoagulation. Advances in Radiation Oncology. 7, 3, 100900 (2022)
- Kamimura S, Suga T, Hoki Y, Sunayama M, Imadome K, Fujita M, Nakamura M, Araki R, Abe M.: Insertion/deletion and microsatellite alteration profiles in induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 16, 2503-2519,(2021)
- Araki R., Hoki Y., Suga T., Obara C., Sunayama M., Imadome K., Fujita M., Kamimura S., Nakamura M., Wakayama S., Nagy A., Wakayama T., Abe M.: Genetic aberrations in iPSCs are introduced by a transient G1/S cell cycle checkpoint deficiency. Nat Commun., 11, 197(2020)
- Fujita M., Imadome K., Somasundaram V., Kawanishi M., Karasawa K., Wink DA.: Metabolic characterization of aggressive breast cancer cells exhibiting invasive phenotype: impact of non-cytotoxic doses of 2-DG on diminishing invasiveness. BMC Cancer. 20, 1, 929 (2020)
- Miura T., Yuasa N., Ota H., Habu M., Kawano M., Nakayama F., Nishihara S.: Highly sulfated hyaluronic acid maintains human induced pluripotent stem cells under feeder-free and bFGF-free conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 18, 3, 506-512 (2019)
- Fujita M., Somasundaram V., Basudhar D., Cheng RYS., Ridnour LA., Higuchi H., Imadome K., No JH., Bharadwaj G., Wink DA.: Role of nitric oxide in pancreatic cancer cells exhibiting the invasive phenotype. Redox biology, 22, 101158 (2019)
- Miura T., Kume M., Kawamura T., Yamamoto K., Hamakubo T., Nishihara S.: O-GlcNAc on PKCζ inhibits the FGF4-PKCζ-MEK-ERK1/2 pathway via inhibition of PKCζ phosphorylation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 10, 1, 272-286 (2018)
- Araki R., Mizutani E., Hoki Y., Sunayama M., Wakayama S., Nagatomo H., Kasama Y., Nakamura M., Wakayama T., Abe M.: The Number of Point Mutations in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Nuclear Transfer Embryonic Stem Cells Depends on the Method and Somatic Cell Type Used for Their Generation. Stem Cells. 35, 1189-1196(2017)
- Araki R., Uda M., Hoki Y., Sunayama M., Nakamura M., Ando S., Sugiura M., Ideno H., Shimada A., Nifuji A., Abe M.: Negligible immunogenicity of terminally differentiated cells derived from induced pluripotent or embryonic stem cells. Nature. 494, 100-4 (2013)
